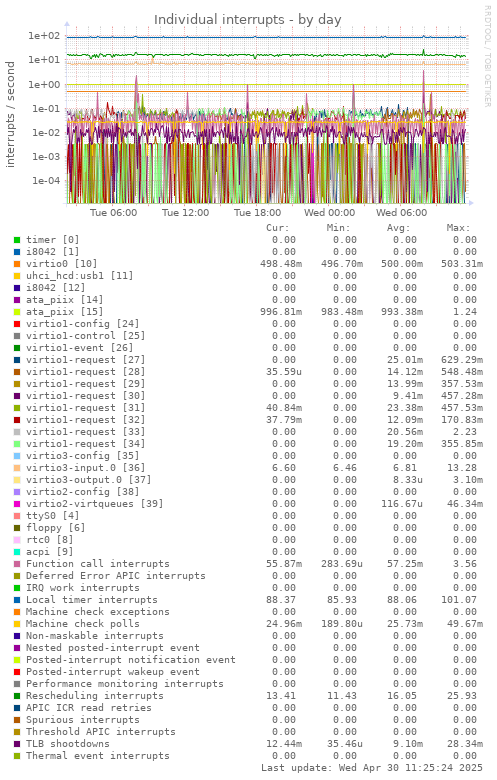
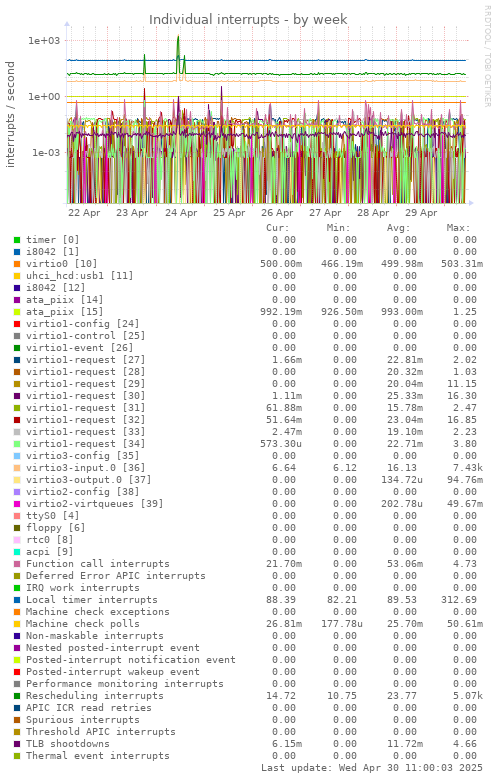
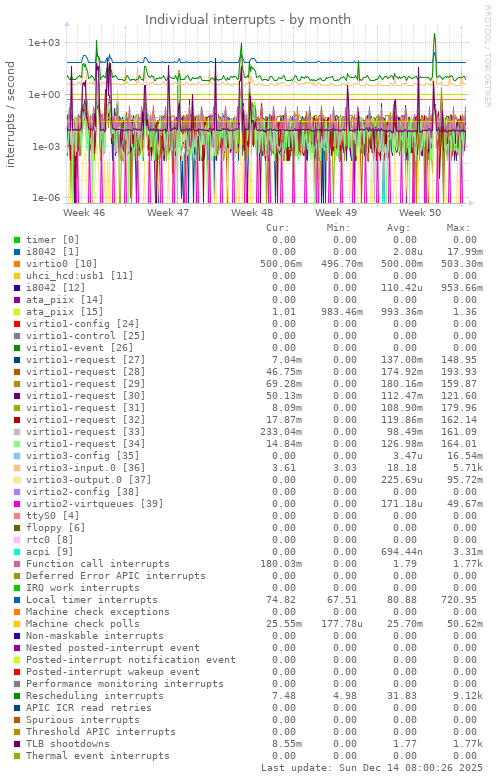
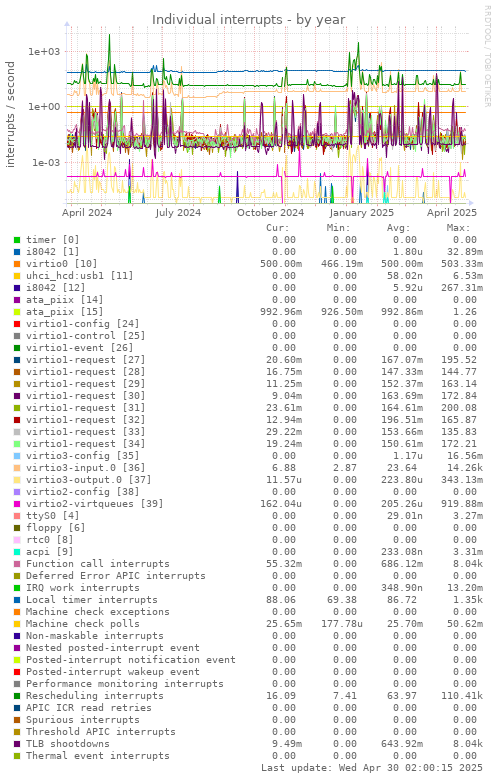
Graph information
Shows the number of different IRQs received by the kernel. High disk or network traffic can cause a high number of interrupts (with good hardware and drivers this will be less so). Sudden high interrupt activity with no associated higher system activity is not normal.
| Field | Internal name | Type | Warning | Critical | Info |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| timer [0] | i0 | derive | Interrupt 0, for device(s): timer | ||
| i8042 [1] | i1 | derive | Interrupt 1, for device(s): i8042 | ||
| virtio0 [10] | i10 | derive | Interrupt 10, for device(s): virtio0 | ||
| uhci_hcd:usb1 [11] | i11 | derive | Interrupt 11, for device(s): uhci_hcd:usb1 | ||
| i8042 [12] | i12 | derive | Interrupt 12, for device(s): i8042 | ||
| ata_piix [14] | i14 | derive | Interrupt 14, for device(s): ata_piix | ||
| ata_piix [15] | i15 | derive | Interrupt 15, for device(s): ata_piix | ||
| virtio1-config [24] | i24 | derive | Interrupt 24, for device(s): virtio1-config | ||
| virtio1-control [25] | i25 | derive | Interrupt 25, for device(s): virtio1-control | ||
| virtio1-event [26] | i26 | derive | Interrupt 26, for device(s): virtio1-event | ||
| virtio1-request [27] | i27 | derive | Interrupt 27, for device(s): virtio1-request | ||
| virtio1-request [28] | i28 | derive | Interrupt 28, for device(s): virtio1-request | ||
| virtio1-request [29] | i29 | derive | Interrupt 29, for device(s): virtio1-request | ||
| virtio1-request [30] | i30 | derive | Interrupt 30, for device(s): virtio1-request | ||
| virtio1-request [31] | i31 | derive | Interrupt 31, for device(s): virtio1-request | ||
| virtio1-request [32] | i32 | derive | Interrupt 32, for device(s): virtio1-request | ||
| virtio1-request [33] | i33 | derive | Interrupt 33, for device(s): virtio1-request | ||
| virtio1-request [34] | i34 | derive | Interrupt 34, for device(s): virtio1-request | ||
| virtio3-config [35] | i35 | derive | Interrupt 35, for device(s): virtio3-config | ||
| virtio3-input.0 [36] | i36 | derive | Interrupt 36, for device(s): virtio3-input.0 | ||
| virtio3-output.0 [37] | i37 | derive | Interrupt 37, for device(s): virtio3-output.0 | ||
| virtio2-config [38] | i38 | derive | Interrupt 38, for device(s): virtio2-config | ||
| virtio2-virtqueues [39] | i39 | derive | Interrupt 39, for device(s): virtio2-virtqueues | ||
| ttyS0 [4] | i4 | derive | Interrupt 4, for device(s): ttyS0 | ||
| floppy [6] | i6 | derive | Interrupt 6, for device(s): floppy | ||
| rtc0 [8] | i8 | derive | Interrupt 8, for device(s): rtc0 | ||
| acpi [9] | i9 | derive | Interrupt 9, for device(s): acpi | ||
| Function call interrupts | iCAL | derive | Interrupt CAL (Function call interrupts) | ||
| Deferred Error APIC interrupts | iDFR | derive | Interrupt DFR (Deferred Error APIC interrupts) | ||
| IRQ work interrupts | iIWI | derive | Interrupt IWI (IRQ work interrupts) | ||
| Local timer interrupts | iLOC | derive | Local (pr. CPU core) APIC timer interrupt. Until 2.6.21 normaly 250 or 1000 pr second. On modern 'tickless' kernels it more or less reflects how busy the machine is. | ||
| Machine check exceptions | iMCE | derive | Interrupt MCE (Machine check exceptions) | ||
| Machine check polls | iMCP | derive | Interrupt MCP (Machine check polls) | ||
| Non-maskable interrupts | iNMI | derive | Nonmaskable interrupt. Either 0 or quite high. If it's normaly 0 then just one NMI will often mark some hardware failure. | ||
| Nested posted-interrupt event | iNPI | derive | Interrupt NPI (Nested posted-interrupt event) | ||
| Posted-interrupt notification event | iPIN | derive | Interrupt PIN (Posted-interrupt notification event) | ||
| Posted-interrupt wakeup event | iPIW | derive | Interrupt PIW (Posted-interrupt wakeup event) | ||
| Performance monitoring interrupts | iPMI | derive | Interrupt PMI (Performance monitoring interrupts) | ||
| Rescheduling interrupts | iRES | derive | Interrupt RES (Rescheduling interrupts) | ||
| APIC ICR read retries | iRTR | derive | Interrupt RTR (APIC ICR read retries) | ||
| Spurious interrupts | iSPU | derive | Interrupt SPU (Spurious interrupts) | ||
| Threshold APIC interrupts | iTHR | derive | Interrupt THR (Threshold APIC interrupts) | ||
| TLB shootdowns | iTLB | derive | Interrupt TLB (TLB shootdowns) | ||
| Thermal event interrupts | iTRM | derive | Interrupt TRM (Thermal event interrupts) |