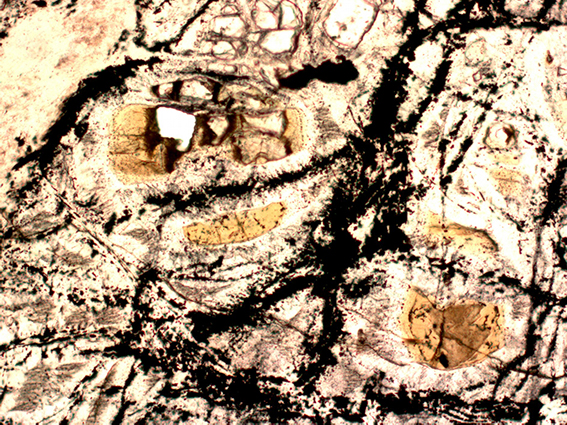
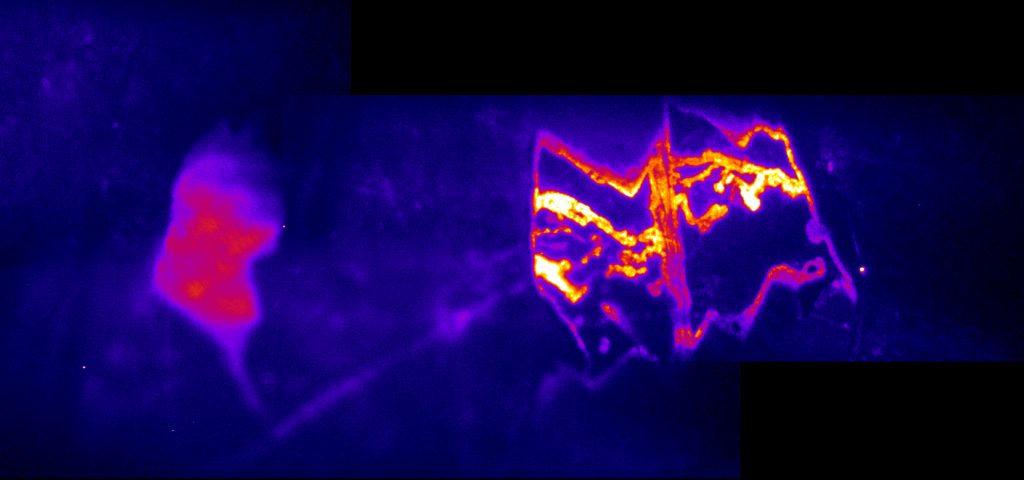
Potential precursors of the first building blocks of life observed in deep ocean rocks
The origin of life on Earth is an extremely complex field of research in which several hypotheses have been put forward. Some studies consider extraterrestrial contributions, via meteorites or asteroids, as a source of organic molecules necessary for the seeding of the Earth. Others believe that our planet has, and had, the potential to produce prebiotic chemistry that was sufficiently efficient to generate the first building blocks of life.
Publication date: 07/11/2018
Press, Research
Related teams :
Lithosphere Organosphere Microbiosphere (LOMs)
Related themes : Origins