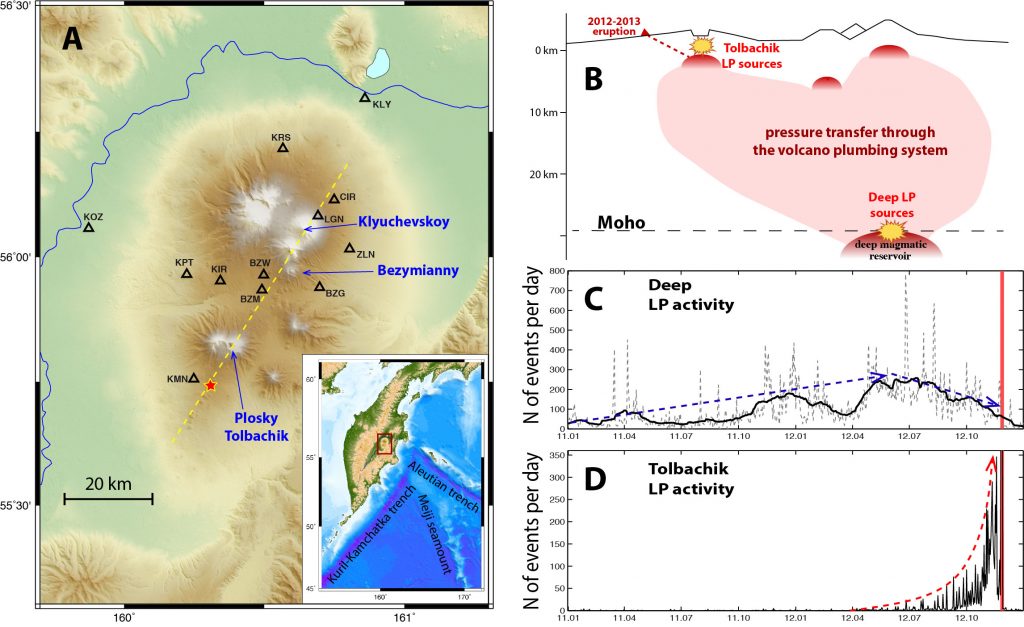
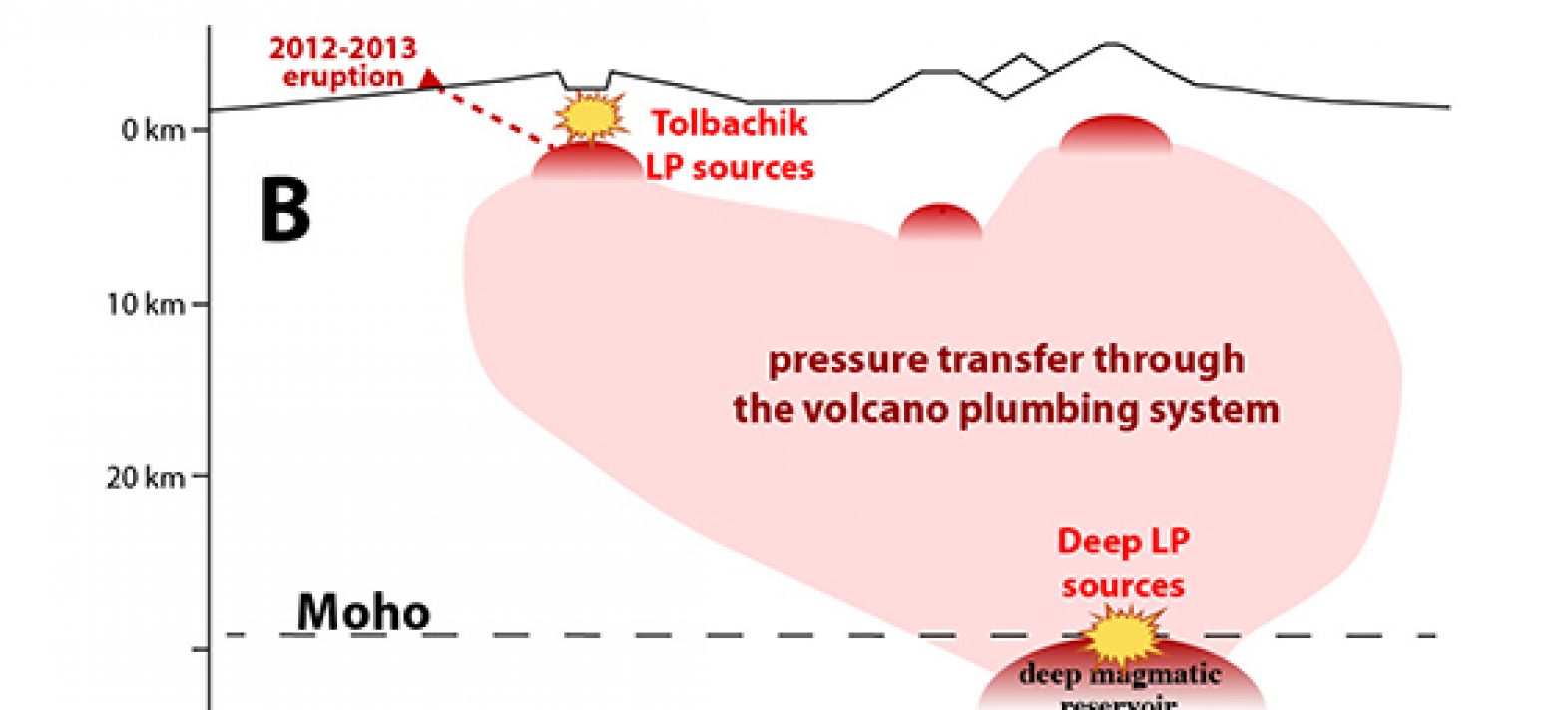
Deep “long-period” earthquakes: early indications of volcano activation
Studying the seismicity of a volcanic area is one of the main methods for studying and monitoring volcanic activity. Indeed, the upwelling of magma from deep magma reservoirs and the pressure changes will cause small earthquakes in the volcanic "plumbing" that can be detected on the surface.
Latest news