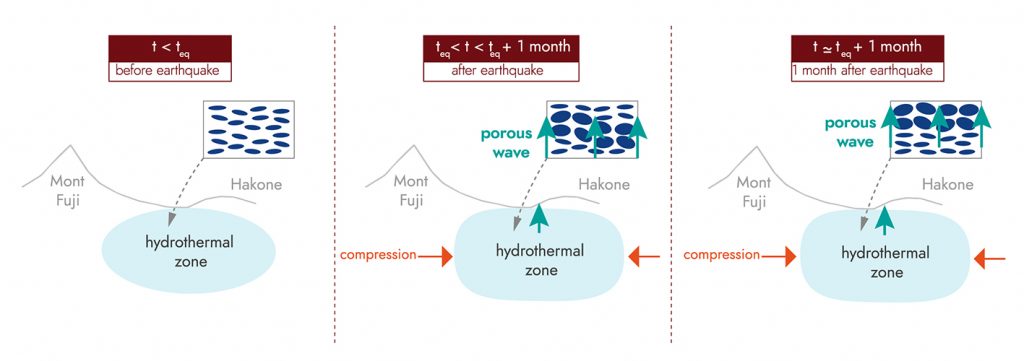
Imaging volcanic disturbances associated with major earthquakes
IPGP researchers and their colleagues have sought to better understand how the 2011 Tohoku megathrust in Japan disrupted volcanic regions, by tracking variations in seismic anisotropy in these areas before and after the quake.

Lake Hakone and Mount Fuji, 19th century print.
Latest news