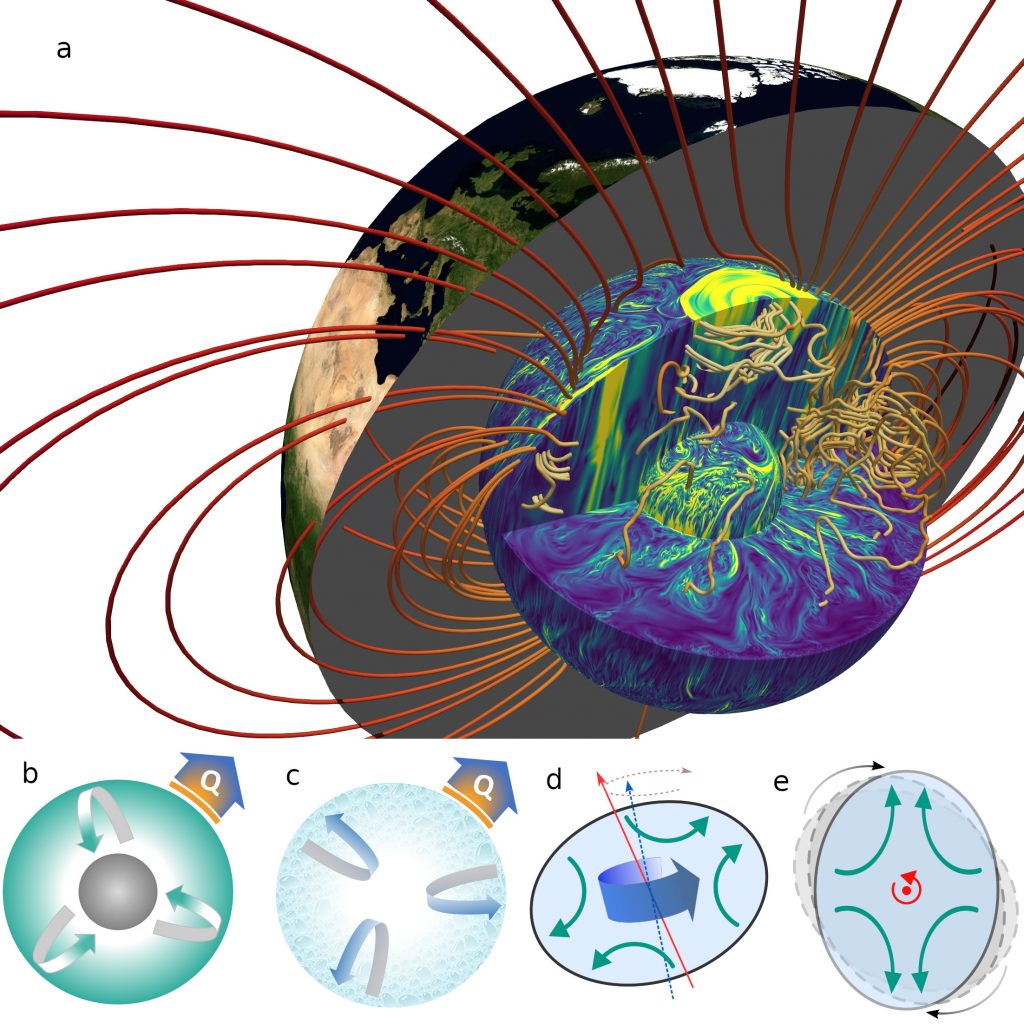
Towards a better understanding of the geodynamic driving force
The Earth's magnetic field is useful for life, enabling many animal and bacterial species to orient themselves in their environment. It is also capable of deflecting the solar wind, leading to the attenuation or amplification of atmospheric erosion.
Publication date: 11/05/2022
Press, Research
Related teams :
Geological Fluid Dynamics
Related themes : Earth and Planetary Interiors