Seismic laws and fractal surfaces
In a recent work, scientists relate the statistical properties of earthquakes (magnitude, frequency, etc.) to those of correlated long-range fractal random surfaces. This relationship makes it possible to understand why and how the different characteristics of earthquakes are statistically related.
Publication date: 04/08/2023
Research
The Earth does not shake at random. By analysing the vast amount of data in seismicity catalogues, it has been possible to empirically determine two key statistical laws describing their characteristics. The Omori law defines the decrease in the number of aftershocks that occur after a major earthquake, while the Gutenberg-Richter law states that the frequency of earthquakes depends on their magnitude. However, the physical processes governing these empirical laws are poorly understood.
In a recent study, a Franco-Japanese collaboration between the Laboratoire de Physique de l’Ecole Normale Supérieure (LPENS), the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris (IPGP), Osaka University and the Laboratoire de Géologie de l’Ecole Normale Supérieure (LGENS), revealed a physical mechanism that could explain the origin of these empirical laws. The scientists used several simplified fault models to reproduce the statistical laws governing earthquakes. They then discovered a fundamental link between these laws and the mathematical properties of the random surfaces representing the fault planes.
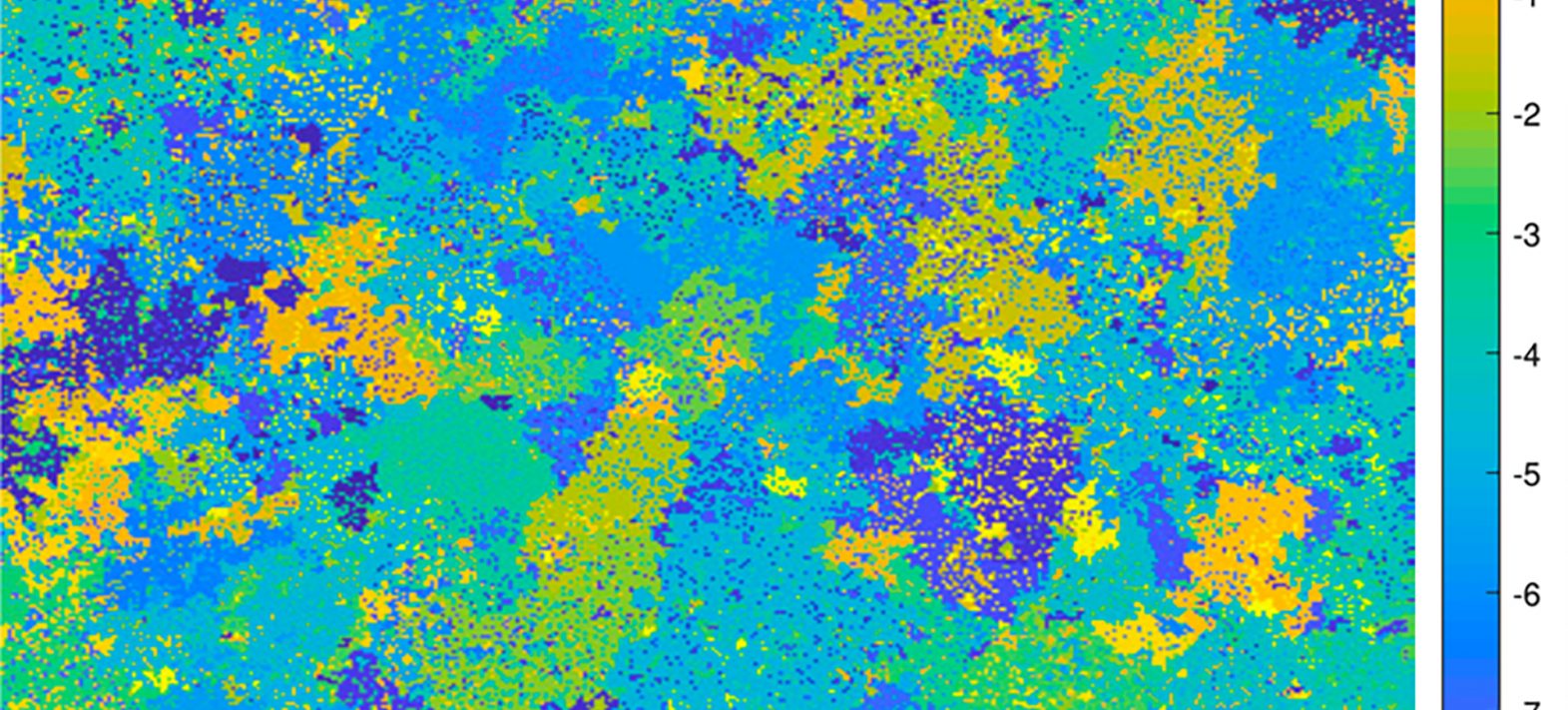
The study reveals that the stress field accumulated on fault planes prior to seismic rupture has a random, self-similar or fractal structure. This stress field retains its characteristics whatever the scale and thus determines the characteristics of large-scale earthquakes. The Gutenberg-Richter and Omori laws can then be explained by the mathematical properties of random surfaces.
These results, published in the journal Physical Review E., open up interesting prospects: an in-depth characterisation of the random surfaces of fault planes could provide a better understanding of the physical processes associated with earthquakes.
> Bibliography :
Earthquake magnitude distribution and aftershocks: A statistical geometry explanation, F. Pétrélis, K. Chanard, A. Schubnel, and T. Hatano, Phys. Rev. E, Published on 22 March 2023 – doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.107.034132
Adapted from the article originally published on the INP-CNRS website: https: //www.inp.cnrs.fr/fr/cnrsinfo/lois-des-seismes-et-surfaces-fractales








