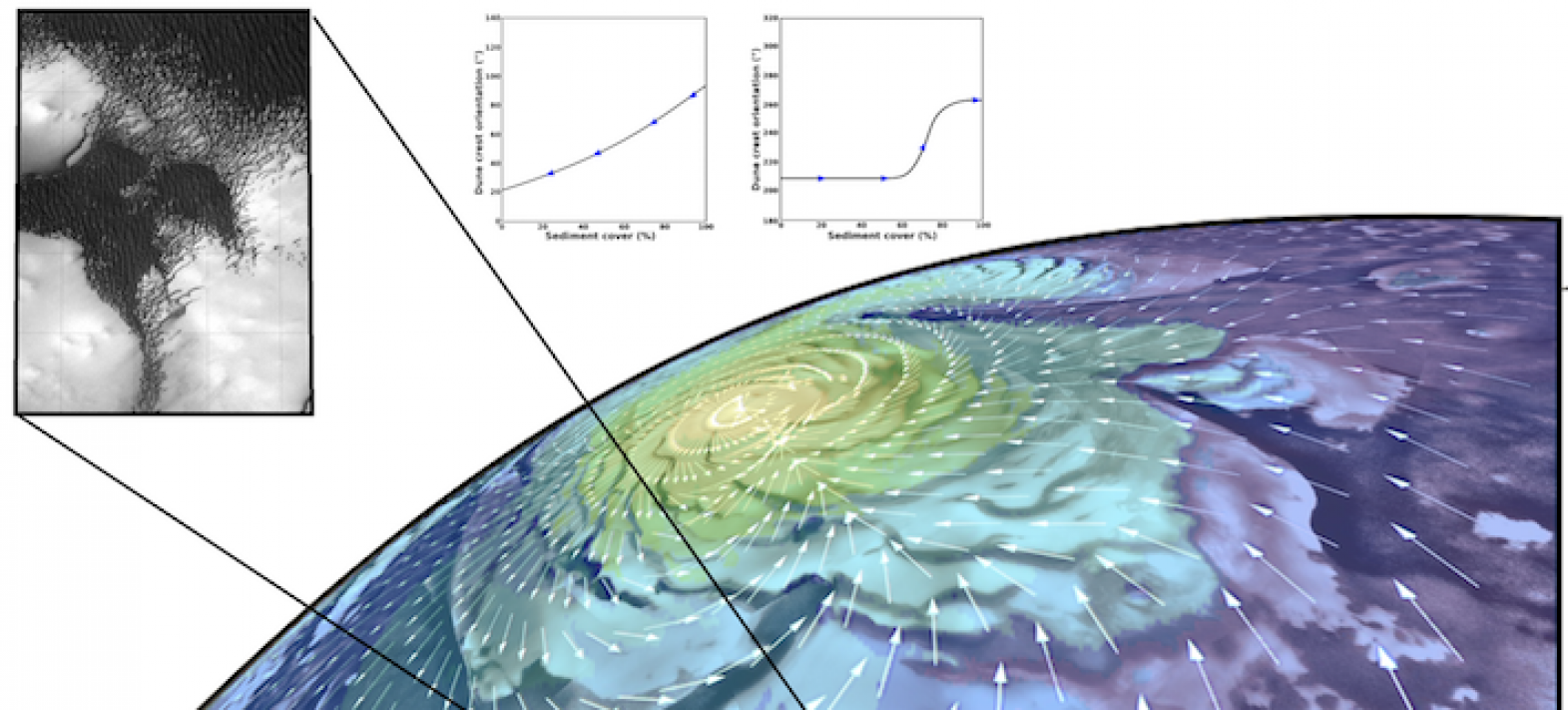
The study of Martian dunes to help better model the global climate circulation of Mars
Dune systems provide unique information about wind regimes on the surface of planetary bodies where there are no direct meteorological data as on Earth. On Mars, in the Olympia Undae region near the northern polar cap, the orientation of the dunes and their sedimentary cover was measured using satellite imagery provided by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter probe by a team of researchers from the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris.
Publication date: 26/04/2018
General public, Press, Research
Related teams :
Geological Fluid Dynamics, Planetology and Space Sciences
Related themes : Earth and Planetary Interiors